-
1 Nov 2025 • Journal Article • Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences
Middle Bronze Age copper smelting in the Wadi Arabah: filling the gap
AbstractDuring the 3rd millennium BCE, major copper smelting activities using wind-powered furnaces took place in the Wadi Arabah, particularly in the Faynan region of Jordan. In the second half of the 2nd millennium BCE, smelting operations at Timna and Wadi Amram, and later in Faynan, employed a different smelting technology, using an artificial air source. Copper smelting
… show more -
23 Oct 2025 • Journal Article • Journal of Animal Ecology
An integrative, peer-reviewed and open-source cooperative-breeding database (Co-BreeD)
AbstractLarge-scale, cross-species comparative analyses on cooperative breeding—where individuals care for the offspring of other group members—are important for understanding sociality and cooperation. However, the datasets that facilitate these analyses are often limited in precision. To advance comparative research on cooperative breeding, we hereby introduce the
… show more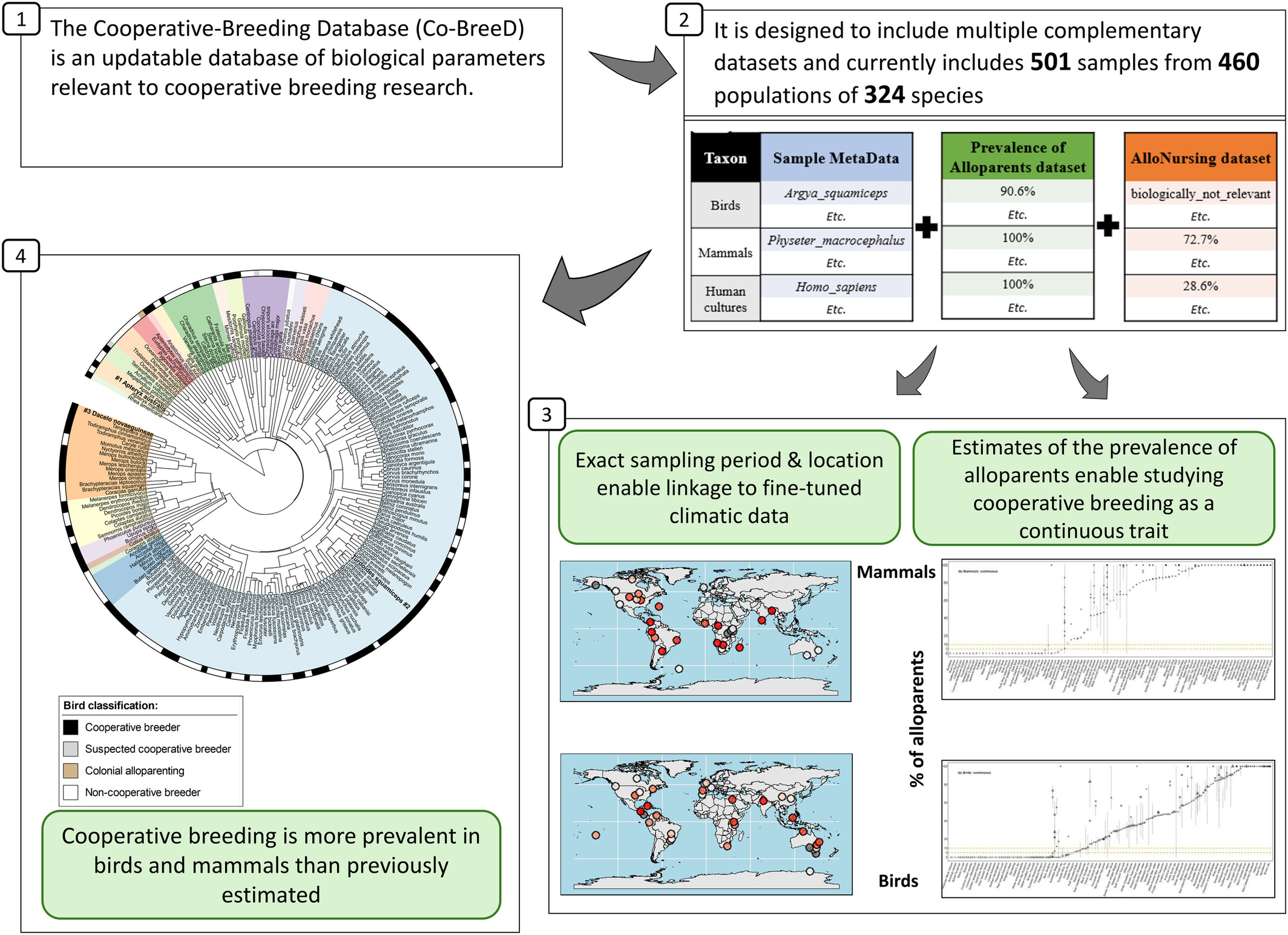
-
14 Oct 2025 • Journal Article • Cells
Oligosaccharyltransferase Is Involved in Targeting to ER-Associated Degradation
AbstractMost membrane and secretory proteins undergo N-glycosylation, catalyzed by oligosaccharyltransferase (OST), a membrane-bound complex in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Proteins failing quality control are degraded via ER-associated degradation (ERAD), involving retrotranslocation to cytosolic proteasomes, or relegated to ER subdomains and eliminated via ER-phagy. Using
… show more
-
13 Oct 2025 • Journal Article • Ornithological Applications
A blessing and a curse: Human resources are beneficial but human presence is detrimental for the growth and development of Argya squamiceps (Arabian Babbler)
AbstractHuman modifications to the environment are having a dramatic effect on biodiversity, but in desert habitats the high abundance of resources near human villages may be beneficial to breeding birds. By collecting high-throughput tracking data on Argya squamiceps (Arabian Babbler), we examined whether nesting and foraging in a village increased nestling growth and development
… show more -
Oct 2025 • Journal Article • Methods in Ecology and Evolution
An active ensemble classifier for detecting animal sequences from global camera trap data
AbstractCamera traps can generate huge amounts of images, and thus reliable methods for their automated processing are in high demand: in particular to find those images or image sequences that actually include animals. Automatically filtering out images that are empty or contain humans can be challenging, as images can be taken in different landscapes, habitats and light
… show more -
15 Sep 2025 • Journal Article • Behavioral Ecology
Complex dynamics of social learning in groups of wild Arabian babblers Open Access
AbstractWe studied the effect of a demonstrator on the learning of a novel foraging task in 12 groups of free-living cooperative breeding Arabian babblers (Argya squamiceps). We allowed naïve babblers to forage jointly on a foraging grid with a demonstrator previously trained to solve a task in one of 2 possible methods: lifting covers of 1 color or pecking through covers of
… show more -
15 Sep 2025 • Journal Article • Environmental Microbiology Reports
The Biology, Microclimate, and Geology of a Distinctive Ecosystem Within the Sandstone of Hyper-Arid Timna Valley, Israel
AbstractMicrobial endolithic communities in the sandstone rocks of the southern Negev Desert, particularly in Timna Park, were initially discovered by Imre Friedmann and Roseli Ocampo-Friedmann in their pioneering study about 50 years ago. Nonetheless, this harsh microecosystem, dominated by cyanobacterial taxa, raises questions about the adaptive mechanisms that enable the
… show more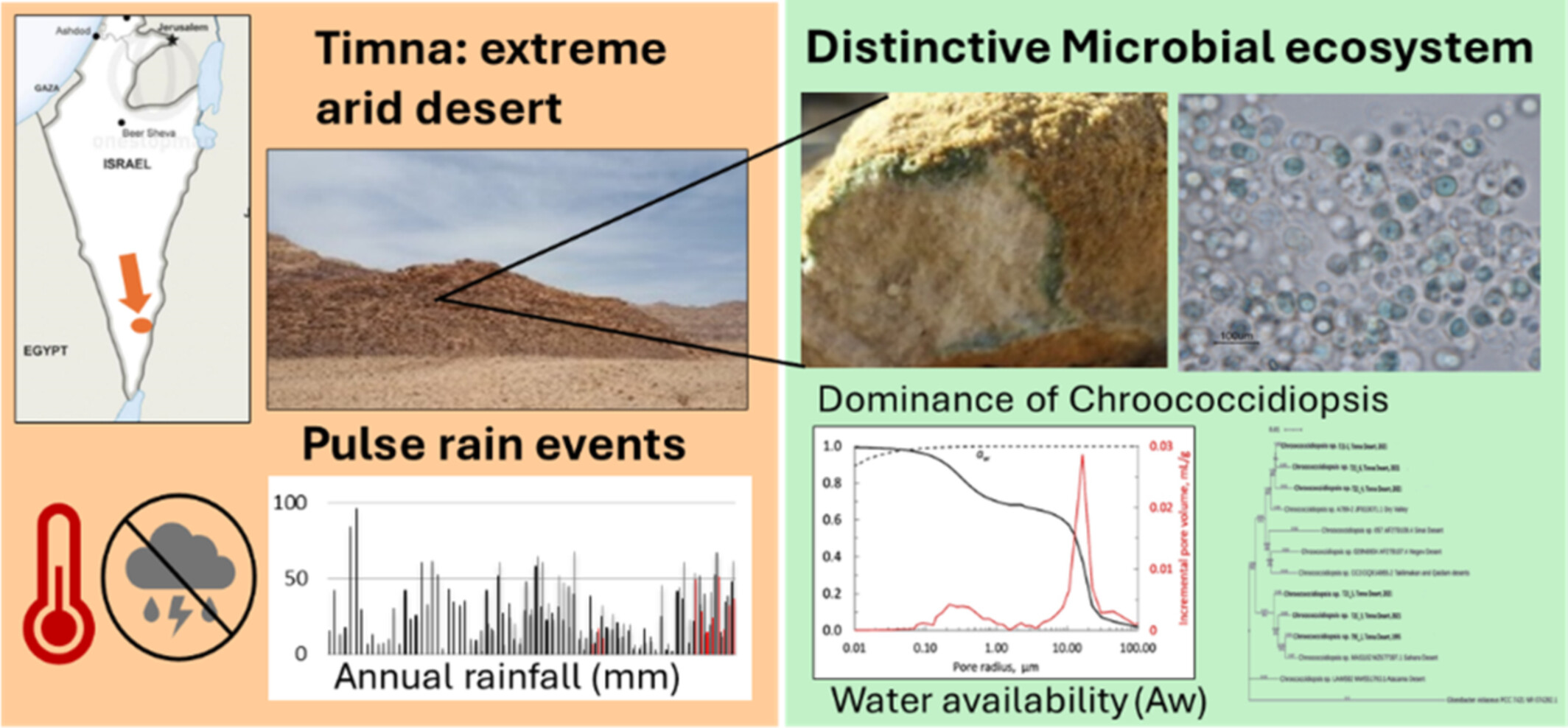
-
4 Sep 2025 • Journal Article • Quaternary Science Reviews
The genesis and environmental context of hypogene-sourced terrestrial carbonates of the middle Pleistocene in Vedi, Ararat Depression
AbstractThe Ararat Depression (Armenia), situated between the southern Caucasus and northern Mesopotamia, holds substantial archaeological Middle Paleolithic sites. However, as paleoclimate archives are scarce in the region, the climatic history is not well constrained. To reconstruct the local paleoclimatic conditions in the past, we studied a ∼30 m-thick sequence of
… show more -
4 Sep 2025 • Journal Article • Conservation Science and Practice
Measuring impact of digital conservation campaigns using culturomics
AbstractConservation campaigns via digital media are becoming increasingly popular amongst conservationists. However, effectively measuring their impacts remains a challenge, and campaign effectiveness often goes unmeasured. Conservation culturomics, which explores the intricate relationship between people and nature in the digital sphere, can help fill this gap. Here, we used
… show more -
29 Aug 2025 • Journal Article • Palestine Exploration Quarterly
Cenotaph Hill: An unknown ‘mound’ in the En-Gedi Oasis
AbstractDespite extensive archaeological explorations in En-Gedi, the largest oasis along the western shore of the Dead Sea, over the past seven decades, a significant component of its settlement landscape has so far gone unnoticed. This component, referred to in this article as Cenotaph Hill, is located in the northern part of the oasis plain, somewhat removed from the nucleus
… show more

















