-
1 Aug 2025 • Journal Article • Marine Environmental Research
Trends in seagrass research in the 21st century – are we there yet?
AbstractDuarte's 1999 review, “Seagrass ecology at the turn of the millennium” established a benchmark for seagrass research. Twenty-five years later, an analysis of 11,245 publications (published between 2000–2023) reveals substantial growth but persistent biases. While the volume of annual publications on seagrasses has increased over this period almost 4 folds, seagrass
… show more -
28 Jul 2025 • Journal Article • Marine Pollution Bulletin
Seagrass as a stabilizing environment for benthic foraminifera living in anthropogenically impacted coastal areas
AbstractIn tropical regions, seagrass meadows provide a unique habitat for benthic foraminifera, both serving as important ecosystem engineers and sensitive indicators of coastal marine ecosystems. However, their interactions remain poorly understood, particularly in the context of anthropogenic pressures and climate change. This study investigates benthic foraminiferal
… show more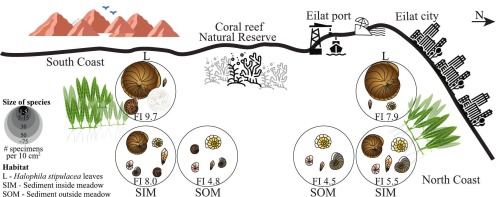
-
2 Jun 2025 • Journal Article • Science of The Total Environment
Transcriptome responses to single and combined stressors in seagrass populations from pristine and impacted sites reveal local adaptive features and core stress-response genes
AbstractIn their natural habitats, seagrasses face multiple abiotic stressors, which can often occur simultaneously. However, most studies have only focused on growth and physiological responses to single stressors. Here, we examined transcriptome responses of the tropical seagrass Halophila stipulacea collected from a northern Gulf of Aqaba pristine site and an anthropogenically-impacted
… show more
-
12 Apr 2025 • Journal Article • Water
A Helping Hand: Fungi, as Well as Bacteria, Support Ecophysiological Descriptors to Depict the Posidonia oceanica Conservation Status
AbstractThe crucial role of plant–microbe interactions in seagrass growth and overall fitness is widely recognized and known to influence plant response to stress. Human-induced changes in coastal ecosystems necessitate efficient descriptors for seagrass monitoring. Recently, for Posidonia oceanica meadows, an integrative approach combining ecophysiological descriptors with
… show more -
Feb 2025 • Journal Article • Open Journal of Ecology
Estimation of Aboveground Biomass of Acacia Trees in the Hyper-Arid Arava, Israel Using Allometric Analysis—Allometric Equations for Acacia Trees in the Desert
AbstractBiomass is among the most important state variables used to characterize ecosystems. Estimation of tree biomass involves the development of species-specific “allometric equations” that describe the relationship between tree biomass and tree diameter and/or height. While many allometric equations were developed for northern hemisphere and tropical species, rarely have
… show more -
21 Oct 2024 • Journal Article • Aquatic Botany
Expansion of Halophila stipulacea in parallel with declines of native seagrasses in the eastern Mediterranean Sea
AbstractSeagrasses native to the Mediterranean Sea are anticipated to be adversely affected by climate warming, while the invasive tropical seagrass species Halophila stipulacea is projected to proliferate and alter the region's underwater seascape. Despite the significant implications of this transition, it is surprisingly rare to include H. stipulacea in long-term monitoring
… show more -
Aug 2024 • Journal Article • Mediterranean Marine Science
Surprising widespread Cymodocea nodosa occurrence along Israel’s Mediterranean coast and Implications for Seagrass Conservation in a hotspot of climate change
AbstractCymodocea nodosa is a temperate seagrass that grows in shallow and sheltered waters of the Mediterranean Sea. Although it is found in both the western and eastern basins, it was thought to be absent from the extremely warm and salty waters along the Israeli coastline, the most eastern part of the Mediterranean. We conducted methodical, seasonal, towed-diver surveys
… show more -
1 Aug 2024 • Journal Article • Environmental and Experimental Botany
Strong regulation of nitrogen supply and demand in a key desert legume tree
AbstractHigh abundance of legumes in drylands suggests that symbiotic nitrogen fixation provides an advantage in water-limited environments. However, the interactive effect of nitrogen availability and water scarcity on the nitrogen fixation strategies of dryland legumes remain largely unexplained. We conducted two experiments to test the effects of nitrogen availability and
… show more -
Apr 2024 • Journal Article • Marine Environmental Research
A matter of choice: Understanding the interactions between epiphytic foraminifera and their seagrass host Halophila stipulacea
AbstractIn sub/tropical waters, benthic foraminifera are among the most abundant epiphytic organisms inhabiting seagrass meadows. This study explored the nature of the association between foraminifera and the tropical seagrass species H. stipulacea, aiming to determine whether these interactions are facilitative or random. For this, we performed a "choice" experiment, where
… show more
-
22 Mar 2024 • Journal Article • Environmental Science & Technology
Impacts of Desalination Brine Discharge on Benthic Ecosystems
AbstractSeawater reverse osmosis (SWRO) desalination facilities produce freshwater and, at the same time, discharge hypersaline brine that often includes various chemical additives such as antiscalants and coagulants. This dense brine can sink to the sea bottom and creep over the seabed, reaching up to 5 km from the discharge point. Previous reviews have discussed the effects
… show more



















