-
23 Oct 2025 • Journal Article • Journal of Animal Ecology
An integrative, peer-reviewed and open-source cooperative-breeding database (Co-BreeD)
AbstractLarge-scale, cross-species comparative analyses on cooperative breeding—where individuals care for the offspring of other group members—are important for understanding sociality and cooperation. However, the datasets that facilitate these analyses are often limited in precision. To advance comparative research on cooperative breeding, we hereby introduce the
… show more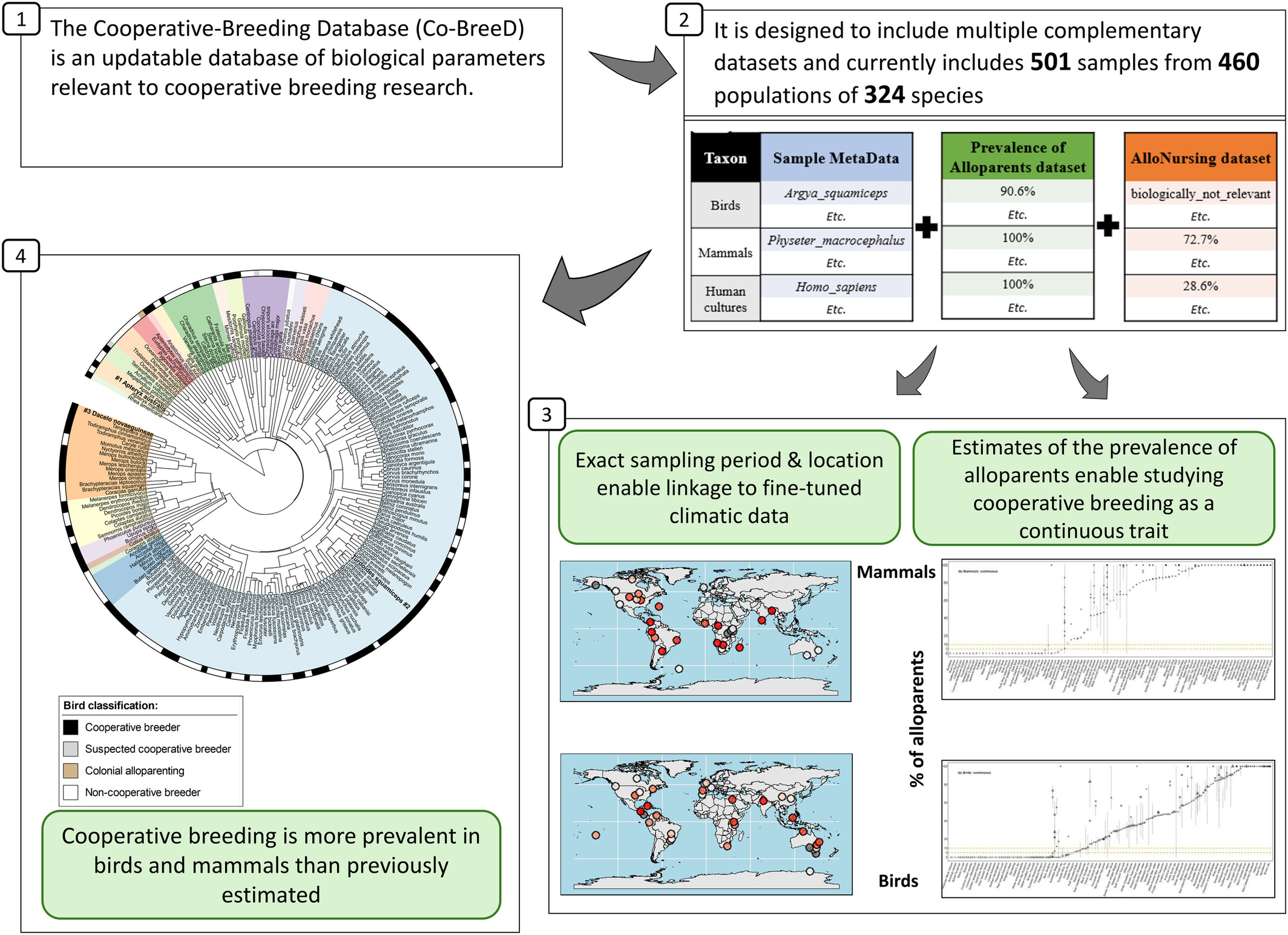
-
13 Oct 2025 • Journal Article • Ornithological Applications
A blessing and a curse: Human resources are beneficial but human presence is detrimental for the growth and development of Argya squamiceps (Arabian Babbler)
AbstractHuman modifications to the environment are having a dramatic effect on biodiversity, but in desert habitats the high abundance of resources near human villages may be beneficial to breeding birds. By collecting high-throughput tracking data on Argya squamiceps (Arabian Babbler), we examined whether nesting and foraging in a village increased nestling growth and development
… show more -
15 Sep 2025 • Journal Article • Behavioral Ecology
Complex dynamics of social learning in groups of wild Arabian babblers Open Access
AbstractWe studied the effect of a demonstrator on the learning of a novel foraging task in 12 groups of free-living cooperative breeding Arabian babblers (Argya squamiceps). We allowed naïve babblers to forage jointly on a foraging grid with a demonstrator previously trained to solve a task in one of 2 possible methods: lifting covers of 1 color or pecking through covers of
… show more -
23 Apr 2025 • Journal Article • Npj Biodiversity
The value of human resources changes with season for a social desert passerine bird
AbstractFor desert species, human development may buffer against resource scarcity by providing reliable resources in an otherwise stark environment. We used high-throughput tracking technology to explore the movement patterns of a social desert passerine bird (the Arabian babbler—Argya quadriceps, Leiothrichidae) in a mosaic of human-modified and semi-natural habitats. From
… show more -
Mar 2025 • Journal Article • Biological Conservation
Compassionate conservation in practice: A values-driven, interdisciplinary, pluralistic, and deliberative community
AbstractConservation biology's purported remit is conserving nature by protecting species, habitats, and ecosystems. Because of this the field has historically given short shrift to the wellbeing of individual animals themselves and their role in nature protection. This approach ignores substantial scientific and ethical evidence showing that many animals are sentient, sapient
… show more
-
1 Aug 2024 • Journal Article • Biological Conservation
Navigating complex geopolitical landscapes: Challenges in conserving the endangered Arabian wolf
AbstractGrey wolf (Canis lupus) populations are beginning to increase globally after centuries of decline. While protective legislations and policy implementations have been driving this increase, evidence suggests that these work because of a general rise in public acceptance of wolves. As people have become more knowledgeable of the important ecological roles played by wolves
… show more -
May 2024 • Journal Article • Ecology Letters
Living fast, dying young: Anthropogenic habitat modification influences the fitness and life history traits of a cooperative breeder
AbstractAnthropogenic habitat modification can indirectly effect reproduction and survival in social species by changing the group structure and social interactions. We assessed the impact of habitat modification on the fitness and life history traits of a cooperative breeder, the Arabian babbler (Argya squamiceps). We collected spatial, reproductive and social data on 572
… show more
-
24 Apr 2024 • Journal Article • Animal Cognition
Proto-tool use for food processing in wild Arabian babblers: matching processing methods, substrates and prey types
AbstractCognition is a powerful adaptation, enabling animals to utilise resources that are unavailable without manipulation. Tool use and food processing are examples of using cognition to overcome the protective mechanisms of food resources. Here, we describe and examine the flexibility of proto-tool use (defined as the alteration of an object through object-substrate
… show more -
Mar 2024 • Journal Article • Frontiers in Bird Science
Using acoustic cameras to study vocal mobbing reveals the importance of learning in juvenile Arabian babblers
AbstractWhen studying bird intra-and inter-specific interactions it is crucial to accurately track which individual emits which vocalization. However, locating sounds of free moving birds (and other animals) in nature can be challenging, especially in situations when many individuals call in spatial and temporal vicinity. In this paper, we will introduce the use of a hand-held
… show more -
24 Jan 2024 • Journal Article • Ecography
Prey responses to foxes are not determined by nativeness
AbstractIntroduced predators are thought to be responsible for the decline and extinction of their native prey. The prey naivety hypothesis provides a mechanism for these declines, suggesting that native prey are vulnerable to introduced predators as their coevolutionary history is insufficiently long for antipredator behaviours to fully develop. The prey naivety hypothesis
… show more










